At the heart of every WordPress website with user accounts lies a
crucial database table:
wp_users. This table is
the central repository for all user-specific information, from login
credentials to display names. Understanding its structure and function
is vital for anyone looking to manage users effectively, troubleshoot
authentication issues, or develop custom WordPress solutions.
1. Introduction
The wp_users table is
one of the core tables created during a standard WordPress
installation. It stores essential information about every registered
user on your site, whether they are administrators, editors,
authors, subscribers, or custom roles.
Why it’s critical for user management, authentication, and custom development:
- User Management: Every time you add, edit, or delete a user through the WordPress admin dashboard, you're interacting with this table behind the scenes.
-
Authentication: When a user attempts to log in,
WordPress queries the
wp_userstable to verify theiruser_login(username) anduser_pass(hashed password). -
Authorization & Permissions: While user
roles and capabilities are primarily managed in
the
wp_usermetatable and defined in WordPress core/plugins, theIDfromwp_usersis the key that links a user to their specific permissions. - Custom Development: Developers often need to interact with this table to retrieve user data for custom features, extend user profiles, or build unique membership functionalities.
Who this guide is for:
This guide is designed for:
- WordPress Developers: Who need to understand the underlying data structure for plugin and theme development.
- Site Administrators: Who may need to perform advanced user management tasks or troubleshoot issues directly in the database.
- Database Professionals: Working with WordPress databases and needing a quick reference to its user schema.
Whether you're looking to understand how WordPress ticks, perform a
specific database operation, or simply expand your knowledge, this
guide will walk you through the ins and outs of the
wp_users table.
2. Where is the wp_users Table Located?
The wp_users table
resides within the WordPress database that powers your website. By
default, WordPress tables are prefixed with
wp_. Therefore, you'll
typically find the users table named
wp_users.
Mention possible prefix changes:
It's important to note that during the WordPress installation
process, or through security plugins, this prefix can be changed.
This is a common security measure to make it slightly harder for
automated attacks to guess table names. If your prefix was changed,
the table might be named something like
wp3_users,
site_users, or
randomstring_users.
You can find your site's specific table prefix by looking in your
wp-config.php file for
the
$table_prefix
variable.
// Example from wp-config.php
$table_prefix = 'wp_'; // This could be different for your siteHow to find it using phpMyAdmin or CLI:
Using phpMyAdmin:
- Log in to your web hosting control panel (e.g., cPanel, Plesk) and open phpMyAdmin.
-
On the left-hand sidebar, select your WordPress database. If you
have multiple databases, you might need to check your
wp-config.phpfile for theDB_NAMEconstant to identify the correct one. -
Once the database is selected, a list of tables will appear in the
main panel. Scroll through this list or use the filter/search box
to find the table ending in
_users(e.g.,wp_users).
Using Command Line Interface (CLI):
For users comfortable with the command line (e.g., via SSH):
- Connect to your server via SSH.
-
Access the MySQL client:
You'll be prompted for your database password.mysql -u YOUR_DATABASE_USER -p YOUR_DATABASE_NAME -
Once connected to the MySQL monitor, list tables matching the user
pattern:
This command will display all tables ending with "users," helping you identify the correct one (e.g.,SHOW TABLES LIKE '%users';wp_users).
3. Structure of the wp_users Table
Understanding the columns within the
wp_users table is key
to comprehending how WordPress stores and manages user data. Below
is a breakdown of the default schema:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ID |
bigint(20)
|
Primary Key. A unique auto-incrementing number assigned to each user. This is the User ID. |
| user_login |
varchar(60)
|
The username chosen by the user for logging in. Must be unique. |
| user_pass |
varchar(255)
|
The user's password, hashed using WordPress's PHPass library (older versions might use MD5). Never stored in plain text. |
| user_nicename |
varchar(50)
|
A URL-friendly version of the username (slug). Often used in
author archive URLs (e.g.,
example.com/author/john-doe).
|
| user_email |
varchar(100)
|
The user's email address. Must be unique. Used for notifications, password resets, etc. |
| user_url |
varchar(100)
|
The user's website URL (optional). |
| user_registered |
datetime
|
The date and time when the user registered. Stored in
YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
format (UTC).
|
| user_activation_key |
varchar(255)
|
A key used for account activation or password reset processes. Cleared after use. |
| user_status |
int(11)
|
Deprecated. This column was historically
used for user status (e.g., spam) but is no longer actively
used by WordPress core. It's typically always
0.
|
| display_name |
varchar(250)
|
The name publicly displayed for the user (e.g., in comments, author bylines). Can be their username, first/last name, or nickname. |
Here's what the
wp_users table
structure might look like when viewed in phpMyAdmin (columns tab):
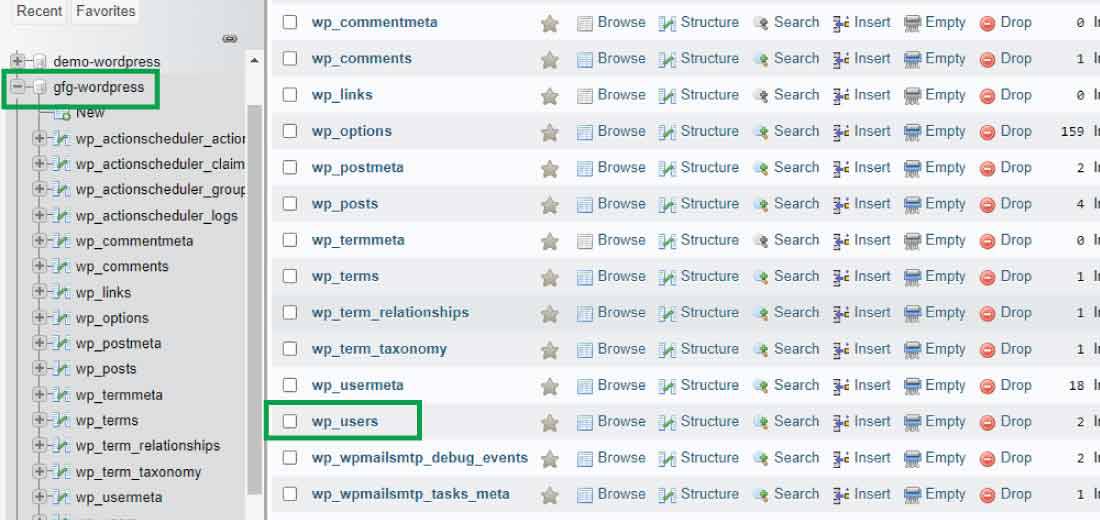
4. Changing User Roles (via
wp_usermeta)
While the
wp_users table stores
the core user identity, user roles and capabilities are primarily
managed in the
wp_usermeta table. To
change a user's role directly in the database, you'll need to update
two specific meta keys for that user's
user_id:
-
wp_capabilities(or[prefix]_capabilities) -
wp_user_level(or[prefix]_user_level)
The meta_value for
wp_capabilities is a
serialized PHP array. The
wp_user_level is an
integer that historically represented a hierarchical level, though
capabilities are more granular and preferred now. Here are the
common values:
| Role |
[prefix]_capabilities
meta_value
|
[prefix]_user_level
|
|---|---|---|
| Subscriber |
a:1:{s:10:"subscriber";b:1;}
|
0
|
| Contributor |
a:1:{s:11:"contributor";b:1;}
|
1
|
| Author |
a:1:{s:6:"author";b:1;}
|
2
|
| Editor |
a:1:{s:6:"editor";b:1;}
|
7
|
| Administrator |
a:1:{s:13:"administrator";b:1;}
|
10
|
Important: Always back up
your database before making direct modifications. Incorrectly
editing serialized data can break user accounts or site
functionality. Using WordPress functions like
wp_update_user()
or
$user->set_role()
in PHP is generally safer if you are working within a WordPress
environment or plugin.